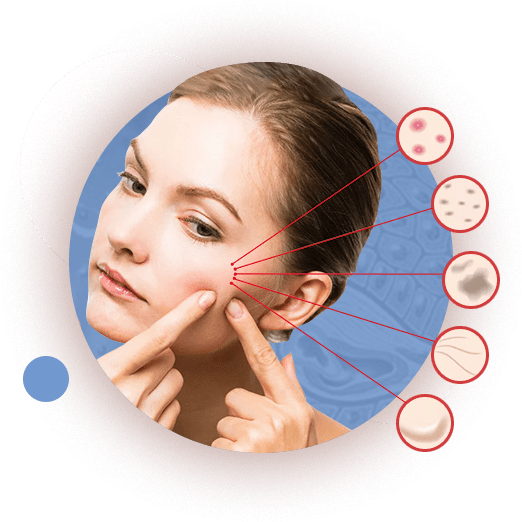
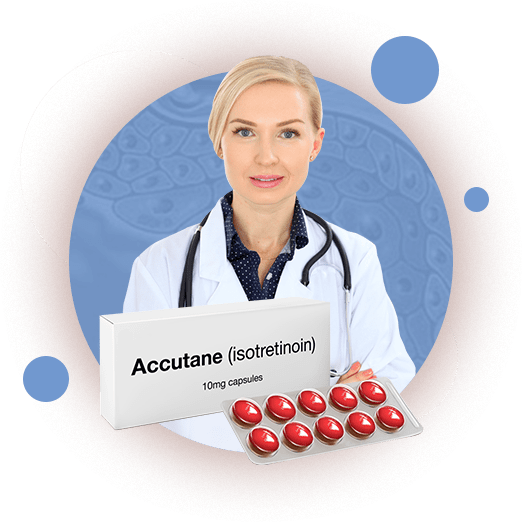
Treatment of mild acne
The choice of the optimal acne treatment regimen is determined by a dermatologist at a personal appointment and is associated with the severity of acne and the individual characteristics of the patient's course of the disease.
Treatment may include therapy with topical drugs (creams, gels, solutions, ointments), as well as drugs for systemic use (capsules, tablets). It is important to know that proper and timely treatment of acne helps to avoid such common complications of the disease as scars, as well as spots of hyperpigmentation (stagnant spots of red-brown color), which over time can develop at the site of acne elements.
For mild acne, when a large number of comedones and single inflammatory elements of acne can be mainly seen on the skin, local preparations for acne therapy and medical cosmetics products specially designed for problem skin care are most often prescribed. Of the local drugs in the treatment of mild acne, topical retinoids (adapalene), benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, as well as combined preparations of adapalene and benzoyl peroxide are more often prescribed. Perhaps a point application of antibacterial drugs to the inflamed elements of the rash.
Treatment of mild acne with topical retinoids
Local retinoids (adapalene) are the most popular group of drugs in the treatment of mild acne. These drugs prevent the formation of comedones (blackheads), and also reduce the formation of sebum. In addition, topical retinoids have an anti-inflammatory effect. The main side effects of topical retinoids are dryness, flaking, and irritation of the skin.
Therefore, in the treatment of mild acne with local retinoids, it is recommended to use moisturizers of medical cosmetics.At the beginning of treatment, it is better to apply retinoids 2-3 times a week, in a thin layer, to allow the skin to get used to the drug. Retinoids increase the sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet light, so care must be taken when treating acne in the summer, and also try not to sunbathe while taking them. Doctors recommend the use of moisturizing sunscreens. It is important to understand that the therapeutic effect with the use of retinoids may be delayed and be noticeable only after 4-6 weeks of using drugs in this group.
Other topical medications to treat mild acne
For mild acne, especially with the appearance of inflammatory elements on the skin, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid, as well as their combinations with adapalene, can also be used. An antibiotic solution can also be applied to the inflamed elements.
Treatment of moderate acne
Treatment of acne of moderate severity, when on the skin, in addition to comedones, you can already notice a fairly large number of inflammatory elements, is usually carried out with local drugs (gels, creams, lotions that are applied to the skin) in combination with systemic drugs (tablets, capsules for oral administration).
Most often, combined preparations of clindamycin and benzoyl peroxide, as well as adapalene and benzoyl peroxide, adapalene and clindamycin are used to treat acne of moderate severity. In addition, topical retinoids (adapalene), antibacterial drugs, benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid can be used. Of the drugs for systemic therapy of acne, after an additional examination of the patient, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial drugs for oral administration, therapy with combined oral contraceptives may be recommended for female patients. Also, if the treatment is ineffective, the dermatologist may recommend therapy with systemic isotretinoin.
The use of local drugs in the treatment of acne of the 2nd degree of severity is based on the inclusion in the treatment regimen of drugs that have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, such as benzoyl peroxide, topical antibiotics, azelaic acid. A combination of several drugs is recommended to enhance the therapeutic effect of each of them.
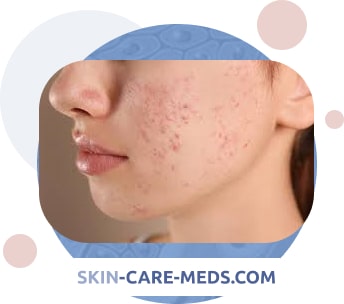
Topical retinoids plus topical antibiotics
Local retinoids (adapalene) in this case help prevent the formation of comedones and reduce the secretion of sebum, their effect may not be noticeable immediately (after 4-6 weeks), but the inclusion of this group of drugs leads to a longer treatment result. And topical antibiotics (clindamycin preparations) help to cope with inflammation, reduce the number of existing elements, and remove redness in the affected area.
Topical antibiotics plus benzoyl peroxide
Topical antibiotics (clindamycin preparations, for example) help reduce inflammation and redness in acne, and comedo formation also decreases against the background of their use. Benzoyl peroxide reduces the risk of resistant strains of microorganisms to topical antibiotics, and in addition, it has an additional anti-inflammatory effect and helps in the fight against comedones.
Local therapy in combination with drugs for systemic use
If acne rashes are common or the effect of the prescribed local treatment is insufficient, the doctor may consider prescribing systemic therapy (antibacterial drugs, combined oral contraceptives in the treatment of women, systemic isotretinoin).
Of the antibacterial drugs for systemic use, tetracycline preparations (minocycline, doxycycline), as well as josamycin preparations, are usually prescribed. In the treatment of acne, systemic antibiotics can be prescribed for a long time - from 6-8 weeks to 4-5 months. Treatment should be strictly under the supervision of a doctor. It is also necessary to avoid the situation of simultaneous use of antibacterial drugs for local and systemic use from different groups.
For female patients, the doctor may prescribe therapy with combined oral contraceptives (COCs). COCs are birth control pills, which usually include ethinyl estradiol and progestin, which lead to a decrease in the level of the male sex hormone testosterone, which reduces the activity of the sebaceous glands and improves skin condition. Most often, so-called microdosed drugs are used in acne therapy, in which the amount of ethinyl estradiol is reduced.
The anti-acne effect of these drugs may not appear immediately, but after about 3-4 months, so contraceptives are prescribed to women for at least six months. Before starting treatment of moderate acne with combined oral contraceptives, women need to consult a gynecologist. During the course of treatment for acne COCs, it is recommended to do a regular blood test to minimize the likelihood of side effects. In view of the delayed therapeutic effect of the use of COCs, it is advisable to use topical drugs during COC therapy, especially in the first months of treatment. The drugs of choice will be those local drugs that can provide a therapeutic effect from the first days of treatment, for example, topical antibacterial drugs.
If the treatment of inflamed acne with the methods described above is ineffective, the doctor may consider the possibility of prescribing systemic isotretinoin preparations. Systemic isotretinoin preparations provide the greatest efficacy in the treatment of acne, as well as a long period of remission after the course of therapy. However, their use requires regular monitoring and possibly strictly under the supervision of a doctor. In the treatment of severe acne with systemic isotretinoin preparations, topical drugs are canceled, except for the situation of temporary exacerbation of acne, which is possible at 2-4 weeks of treatment. In this case, it is possible to prescribe topical antibacterial drugs for a period of 2-3 weeks pointwise to the elements of acne.
Treatment of severe acne
In the treatment of severe acne, when the disease is pronounced, acne affects large areas of the skin, and is also characterized by a large number of inflammatory elements, therapy is carried out with the mandatory use of drugs for systemic acne therapy. The drugs of choice in this case are isotretinoin preparations for systemic use (capsules, tablets).
If treatment with systemic isotretinoin is not possible for any reason, the doctor can choose a combination therapy by combining drugs for systemic acne therapy (antibacterial drugs, combined oral contraceptives for female patients), as well as drugs for local acne therapy (benzoyl peroxide, adapalene preparations, topical antibacterial drugs).
In the treatment of severe acne with systemic isotretinoin preparations, other drugs for systemic and topical use are canceled, except for the situation of temporary exacerbation of acne, which is possible at 2-4 weeks of treatment. In this case, it is possible to prescribe topical antibacterial drugs for a period of 2-3 weeks pointwise to the elements of acne.
Isotretinoin
The active ingredient of a number of drugs belongs to a group of substances called retinoids. The representative of retinoids for the topical treatment of severe acne is a group of drugs based on adapalene, in the systemic therapy of acne, isotretinoin-based drugs are used.
Isotretinoin acts on all the main stages of acne development, as a result of which it provides the maximum therapeutic effect in the treatment of this disease.
In the human body, isotretinoin affects the function of the sebaceous glands (reduces the secretion of the sebaceous glands, reduces the size of the glands), has an effect on the maturation of skin cells and the sebaceous hair follicle (hyperkeratinization is eliminated, the processes of maturation and division of skin cells are normalized), has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, and also has antibacterial and antiandrogenic effects.
Adapalene-based drugs are the drugs of choice in the treatment of mild acne.
Systemic isotretinoin preparations are the most preferred method of treating severe acne, as well as in a situation where moderate acne cannot cope with the disease with standard methods of therapy.
Treatment of grade 3 acne with systemic isotretinoin can lead to clinical recovery of the patient and long-term remission of the disease, but the maximum therapeutic effect of treatment with systemic isotretinoin can be expected if the correct duration of treatment with the drug (6-9 months) is observed and the doctor's recommendations for the daily dosage of the drug are strictly followed. It is not recommended to take breaks in treatment with the drug for more than a day due to an increased risk of recurrence of the disease with an intermittent course of treatment with this drug.
In the treatment of grade 3 acne with the use of systemic isotretinoin, the patient must be examined before prescribing the drug to exclude contraindications to the use of systemic isotretinoin by the doctor, as well as regularly take a biochemical blood test during treatment to monitor the tolerability of therapy by the doctor.
Treatment of severe acne with systemic retinoids is absolutely contraindicated in pregnant women. Therefore, those women who have been prescribed isotretinoin for systemic use should use effective contraceptives one month before the start of the drug, during the entire course of treatment, as well as within one month after its completion.
During therapy with systemic retinoids, the sensitivity of the skin to ultraviolet light increases, which makes it necessary to limit exposure to the sun and in the solarium for the entire period of treatment.
Against the background of treatment with systemic retinoids, joint pain can be observed during heavy physical exertion. In this connection, it is recommended to limit intense exercise and weight lifting during treatment with the drug.
Also, all patients with systemic isotretinoin therapy should limit alcohol consumption for the entire period of therapy with the drug, as well as reduce the consumption of very fatty foods and fast food in the diet.
Therapy with systemic isotretinoin is well predicted in terms of potential therapeutic effect and tolerability of treatment. At the same time, it is very important to follow the rules for the use of the drug, as well as regularly come to an appointment with a specialist. Recently, there have been additional opportunities to monitor systemic isotretinoin therapy by both the doctor and the patient (a mobile application that allows you to remember the rules for taking the drug, as well as track the dynamics of recovery and tolerability of treatment).
 DE
DE FR
FR IT
IT ES
ES